# Tooling
# Tools to install
TIP
If it is allowed by your local security policy, it is recommended to work under a Linux VM, for example Dev-Box MTS, to get a better development experience. This is not mandatory for this training though.
# Node.js
Install Node.js (preferably latest version, minimum version 8.x). You can use nvm if you need to manage different versions of Node.js on your local machine.
# Visual Studio Code and Vetur
During the training you will need a solid JavaScript code editor.
We recommend Visual Studio Code, a fairly lightweight free editor that is now very popular in the JavaScript community.
VS Code has many extensions to enrich the experience. Install the Vetur extension that will help the editor manage the syntax of the * .vue component files.
# Vue Devtools
Download the extension vue-devtools available on Chrome, Firefox or as a standalone application. This will help you debug your code during the practical work.
# Vue CLI
Now, let's install the tools needed to develop Vue.js projects on your machine:
We will need to install the command line utility called Vue CLI. This utility makes it much easier to create and configure Vue projects.
From your Terminal, run the following command to install @vue/cli in global dependency:
npm install -g @vue/cli
You now have access to the vue command from a terminal. Try it to check the installation and to have more information about the available commands:
$ vue
Usage: vue <command> [options]
Options:
-V, --version output the version number
-h, --help output usage information
Commands:
create [options] <app-name> create a new project powered by vue-cli-service
add [options] <plugin> [pluginOptions] install a plugin and invoke its generator in an already created project
invoke [options] <plugin> [pluginOptions] invoke the generator of a plugin in an already created project
inspect [options] [paths...] inspect the webpack config in a project with vue-cli-service
serve [options] [entry] serve a .js or .vue file in development mode with zero config
build [options] [entry] build a .js or .vue file in production mode with zero config
ui [options] start and open the vue-cli ui
init [options] <template> <app-name> generate a project from a remote template (legacy API, requires @vue/cli-init)
config [options] [value] inspect and modify the config
upgrade [semverLevel] upgrade vue cli service / plugins (default semverLevel: minor)
info print debugging information about your environment
Run vue <command> --help for detailed usage of given command.
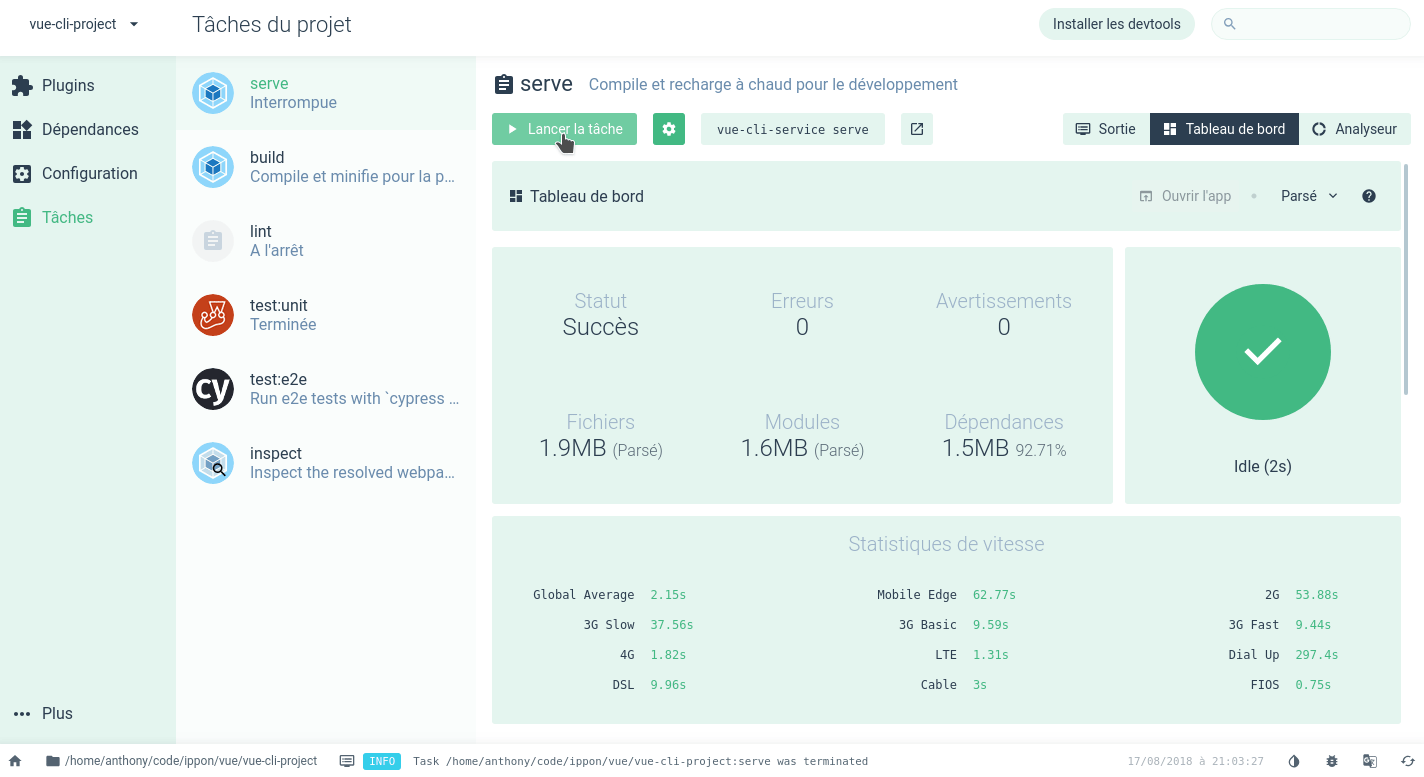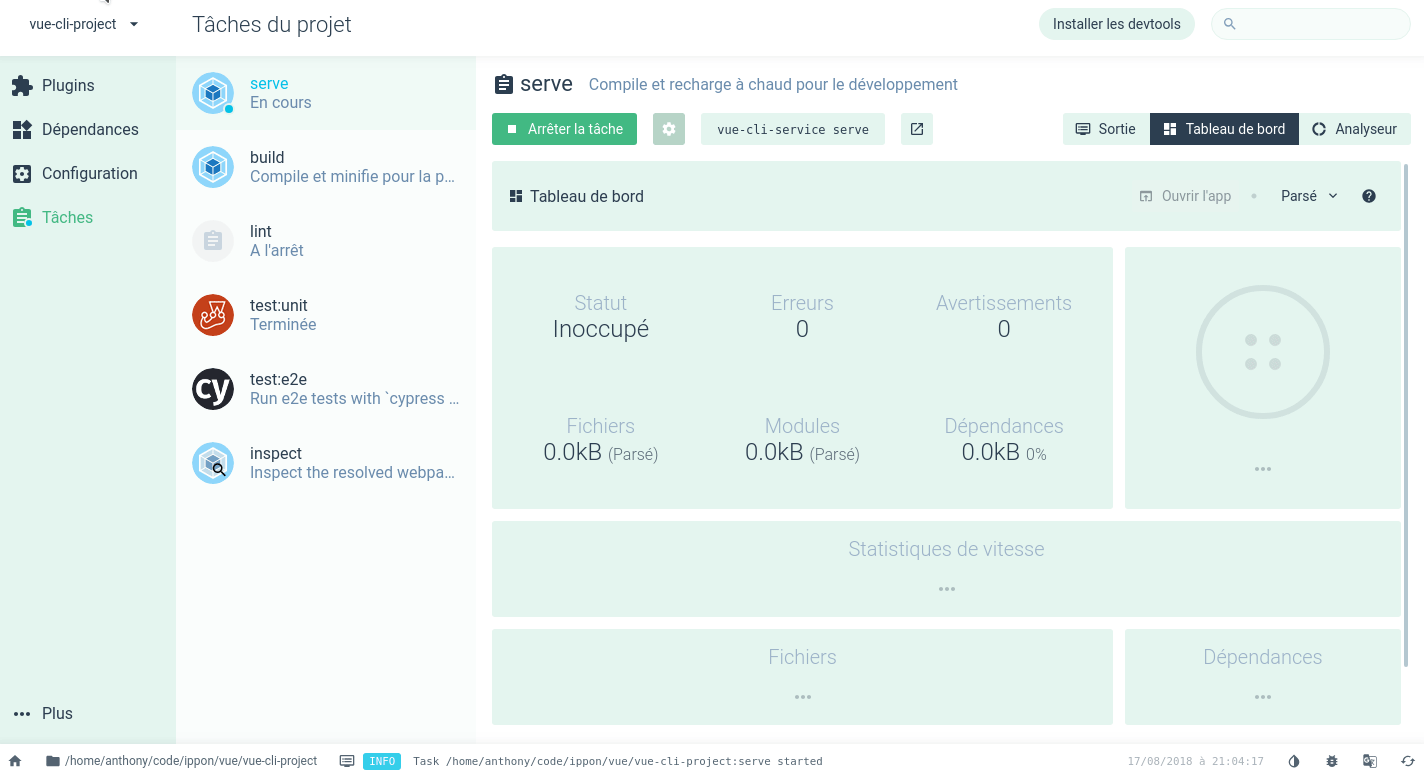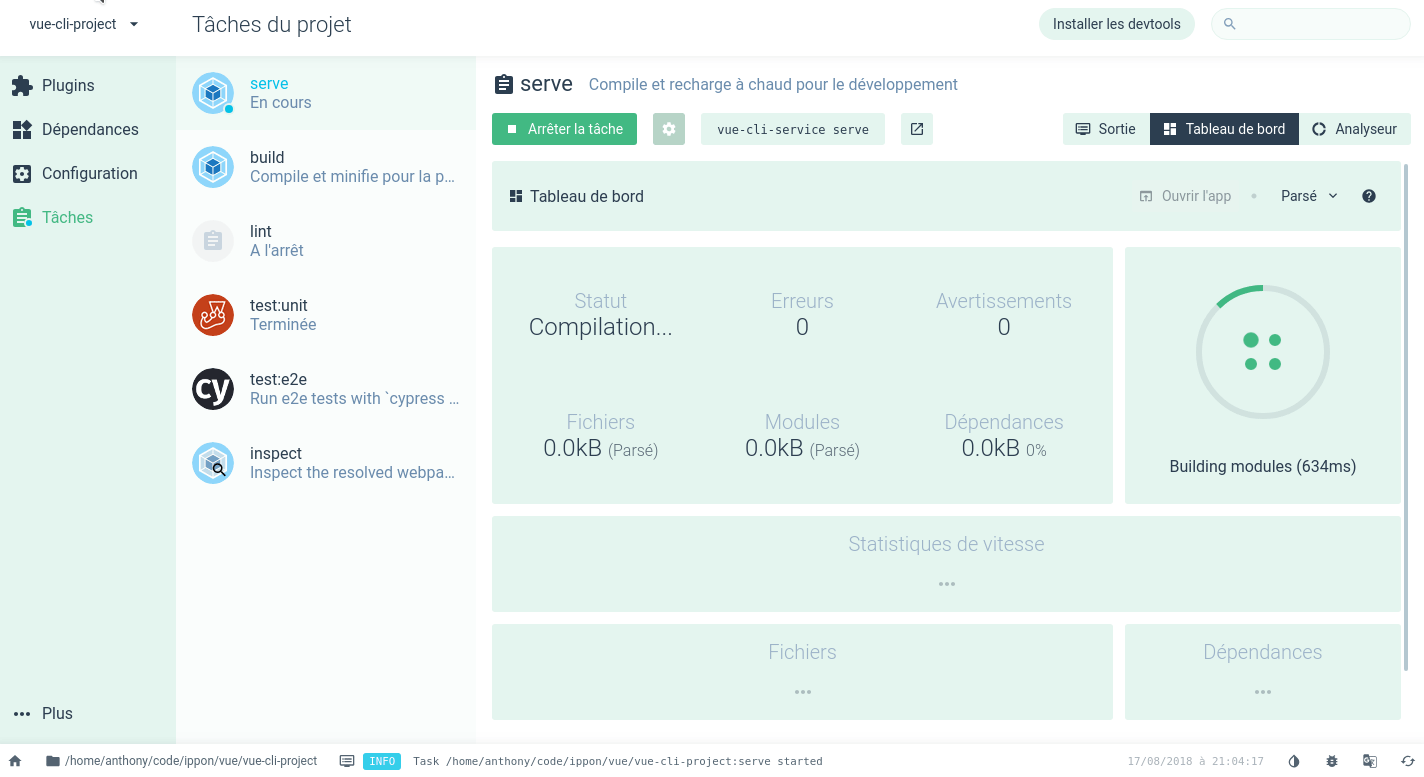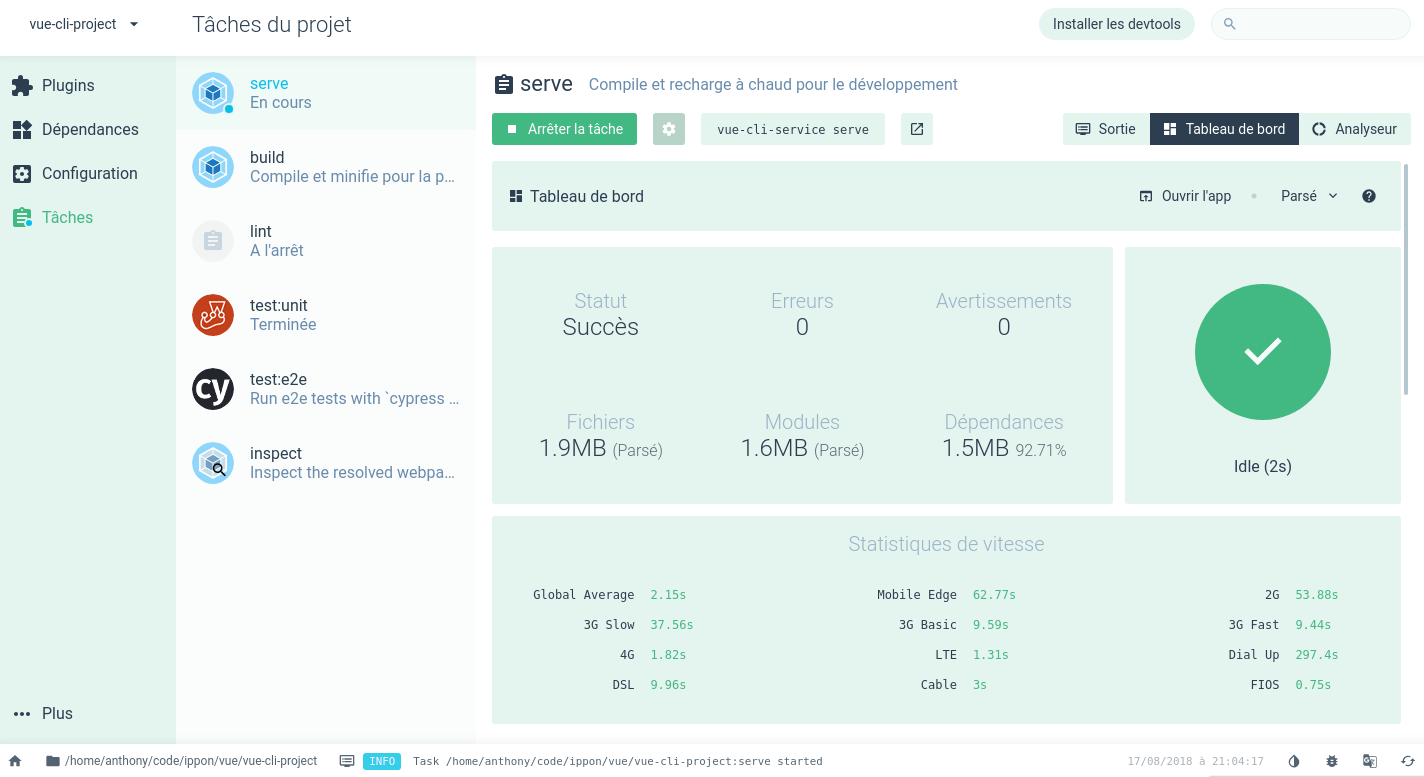
The vue ui command is very useful for beginners: it provides a browser-based graphical user interface for managing a Vue project. The UI can replace the command line for many tasks, such as:
- create or import a Vue project
- add plugins to your project
- configure your project tools
- launch the application
- run unit tests
- etc.
# Vue.js without build step (runtime only)
It is possible to use Vue.js without all this tooling on the developer's workstation. Vue is basically a JavaScript library that can be imported and used directly on clients' browsers.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>Hello Vue</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>Hello {{name}} !</h1>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({ el: "#app", data: { name: "Vue" } });
</script>
</body>
</html>
However, this usage quickly finds its limits, and the development tools that come with Vue projects prove to be very valuable over time. But this can be useful if you want to integrate Vue components into a project made with another framework, or if you want to make a quick prototype.
# Practical Work: Create your first project
Get into your workspace and create a project called search-films by running the following command:
vue create search-films
search-films being the name of the directory in which our project will be created.
Choose the following configuration:
@vue/cli 4.5.6
? Please pick a preset: Manually select features
? Check the features needed for your project: Babel, Linter, Unit
? Choose a version of Vue.js that you want to start the project with (Use arrow keys): 2.x
? Pick a linter / formatter config: ESLint with error prevention only
? Pick additional lint features: Lint on save
? Pick a unit testing solution: Jest
? Where do you prefer placing config for Babel, PostCSS, ESLint, etc.: In dedicated config files
? Pick the package manager to use when installing dependencies: Use NPM
- Babel is a toolchain that is mainly used to convert ECMAScript 2015+ code into a backwards compatible version of JavaScript in order to support as many browser as possible.
- ESLint is a tool for identifying and reporting on patterns found in ECMAScript/JavaScript code, with the goal of making code more consistent and avoiding bugs.
- Jest is a JavaScript testing framework with a focus on simplicity.
At the end of the installation, a folder has been created for your project. Navigate to the directory of your project:
cd search-films
# Work in developer mode
To work on the application and test it live, run the following command:
npm run serve
Your application is accessible on localhost:8080 (default port if available).
In Visual Studio Code, open the project folder and browse through the different files to visualize of the project tree.
# Build for production
You can at any time package your project for production by running:
npm run build
This command will compile your project using Webpack in production mode. Webpack is a bundler, a tool that will transform your sources into a small number of bundles, optimized and compressed JS and CSS files, and put them in the /dist folder of your project. You can then deploy this folder on a file server such as Apache or nginx.
TIP
Basic Vue CLI commands are listed in the README.md generated at the root of the project
# Project configuration
You can configure your Vue project in multiple ways, for example by changing the port used by the development server. At the root of the project, create a vue.config.js file, and put the following content in it:
module.exports = {
devServer: {
port: 3000
}
};
Your project will now be accessible on port 3000 in developer mode. See the configuration documentation for more information about the available options.